Day 1 :
Keynote Forum
Edislav Leksic
Almac Group, UK
Keynote: Understanding the importance of diversity of particle size methods based on laser diffraction
Time : 09:30-10:15

Biography:
Edislav Lekšić is the Team Leader of Physical Sciences at Almac Sciences. He has worked in the pharmaceutical industry for the past 12 years, with expertise in solid state chemistry related to API selection, crystal surface property, scale-up and production troubleshooting. He has been involved in preformulation work and development of systems such as solid dispersions and cocrystals. He has worked closely with patent law authorities contributing to aspects of IP. He has a strong GMP background and experience in XRPD and PSD method validation and transfers. He received a PhD in supramolecular chemistry from the University of Zagreb.
Abstract:
It is known that particle size can play a significant role on drug substance and product performance (e.g. solubility) and manufacturability (e.g. flowability). Due to low water solubility, in most cases particle-size distribution (PSD) methods intend to measure primary particles in the bulk as there is direct correlation of particle size and kinetics of solubility. For the release methods, the decision on what aspects of particles a given PSD method should measure is ideally based on the Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP) of the drug product. The measurement of agglomerates in the bulk is crucial for formulations where agglomerates remain intact due to their hardness. PSD methods are useful for processes monitoring such as micronization or drying, where secondary agglomeration might happen for controlling process modifications (process improvement) including scale-up processes. PSD methods are sometimes selected as tests involved in stability protocols with reference to the results observed for batches used in bioavailability or clinical studies for drug self-life determination. For more challenging active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) regarding bulk properties, a batch-to-batch comparison method might be suitable to distinguish between batches. The different types of PSD methods mentioned above can be applied during different project stages (R&D and GMP) and for different purposes. Such diversity of PSD methods, as well as the fact that there is no general PSD method listed in any pharmacopoeia, might confuse programme leaders and manufacturers. This lecture gives overview on basic principles of PSD methods based on laser diffraction and stress the challenges during method development and method transfers.
Keynote Forum
Lisa Elviri
University of Parma, Italy
Keynote: Liquid chromatography-electrospray-mass spectrometry lipid profile of human fibroblast cells exposed to 3D printed chitosan scaffolds developed for soft tissue regeneration
Time : 10:15-11:00

Biography:
Lisa Elviri has completed her PhD at Parma University, IT in 2001. She is an Associate Professor of Analytical Chemistry at the Food and Drug Department of the University of Parma. She works mainly on sample preparation, liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry based techniques, 3D printing and biomaterial for regenerative medicine. She has over 90 publications that have been cited over 2300 times, and her publication H-index is 27. She is the Founder and President of M3datek Srl an innovative start-up dedicated to the 3D printing of biomaterial-based medical devices for regenerative medicine.
Abstract:
Tissue engineering is a promising field of regenerative medicine that relies on the developing synthetic or naturally-derived biological substitutes (scaffolds) capable to help injured tissues to heal properly. Polymeric materials are often selected as promising candidates for scaffolding thanks to their high surface-to-volume ratio, their structural similarity to the matrix and in function of their final biomedical purpose. Furthermore, 3D biomaterial manufacturing strategies show an extraordinary driving force for the development of innovative therapies in the tissue engineering field, based on the interaction of three main elements: a supporting material, growth factors, and cells. Interaction mechanisms are the entanglement of macromolecules, lipids and interdigitation of the ECM with the physical biomaterial 3D structure, for example, pores. Here, the lipid profile of human fibroblast cells growth on 3D printed chitosan (CH) scaffolds was explored in terms of qualitative and quantitative profile, as a function of the time. Lipids play multiple roles within cells, such as those in energy storage, autocrine and paracrine signaling, and autophagy. Scaffolds were made by a home-made 3D cryo-printing process from formulations at the 6% w/w of chitosan, gelled in 1.5 M potassium hydroxide. Human fibroblast were grown on the 3D scaffolds and the lipid extraction was carried out by evaluating the performance of three different exctration protocols: butanol/methnol (BUME), metyl-tert-buthyl ether (MTBE) and hexane/isopropanol (HI). Three different classes of lipids were analyzed: fatty acyls, phospholipids and sterol lipids by liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. The results will be presented and discussed as a function of the extraction protocol, the scaffold properties and the growing time.
- Analytical Chemistry | Drug Discovery and Development | Drug Analysis | Analytical Method Development and Validation | Chemical Imaging | Chromatography & Separation Techniques | Biosensors in Analytical Chemistry | Pharmaceutical Chemistry | Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology | Modern Pharmaceutical Analysis
Location: Goya

Chair
Michael Petri
Lake Constance Water Supply, Germany
Session Introduction
Michael Petri
Lake Constance Water Supply, Germany
Title: Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and transformation products in raw and treated drinking water in Lake Constance
Time : 11:30-12:00

Biography:
Michael Petri is Laboratory Manager at the Chemical Analysis Department of Lake Constance water supply. He has a PhD from Glasgow Caledonian University and more than 20 years of experience in organic and inorganic analysis of surface, ground and drinking water.
Abstract:
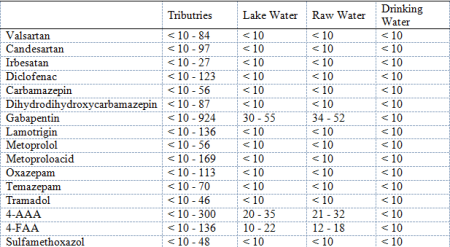
The occurrence of 36 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in surface and treated drinking water of Lake Constance was investigated. Lake Constance is the third largest lake in Europe and located at the northwest edge of the Alps. 17 drinking water suppliers withdraw about 170 million cubic meters of surface water from Lake Constance to serve more than five million people with drinking water. Over 95% of the wastewater in the catchment area of Lake Constance is treated before entering the lake. Pharmaceuticals which are not removed efficiently by waste water purification are discharged into receiving waters and can reach the water of Lake Constance. Therefore, it is useful to investigate the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in the surface water and in the treated drinking water of Lake Constance. Water samples were taken from 17 different tributaries, from the lake water (depth profile) and raw- and drinking water from Lake Constance water supply. The samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography with high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS, Q Exactive and Thermo-Fisher Scientific) after filtration and direct-injection (DI). The limit of quantification of all pharmaceuticals for the DI-LC-HRMS method is 10 ng L-1. In the tributaries 16 of 36 investigated pharmaceuticals and transformation products were detectable in concentrations up to 169 ng L-1. 4-acetylaminoantipyrine (4-AAA) and gabapentin could be measured in concentrations even up to 300 ng L-1 and 924 ng L-1, respectively. In lake water and in the raw water of Lake Constance water supply only 4-acetylaminoantipyrine, 4-formylaminoantipyrine (4-FAA) and gabapentin were detectable in concentrations between 10 and 55 ng L-1. At Lake Constance water supply, the raw water is drawn from a depth of 60 m and is treated with ozone and rapid sand filtration. In drinking water all investigated pharmaceuticals were much below the limit of quantification (10 ng L-1).
Vitali M Boitsov
Saint-Petersburg Academic University, Russia
Title: Synthesis of novel spiro-fused cyclopropa[a]pyrrolizines and 3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes and evaluation their antitumor activity
Time : 12:00-12:30
Biography:
Vitali M Boitsov is an Associate Professor in the Saint-Petersburg Academic University, Russian Federation. He has completed his PhD in Organic Chemistry in 2005 from the Saint-Petersburg State University, Russian Federation.
Abstract:
Oncological diseases are one of the most common public health problems and a major cause of mortality. Increasing drug resistance and development of tumor resistance as well as severe side-effects of chemotherapeutic agents reduce the clinical efficacy of currently used anticancer drugs and therapies. Despite the increasing use of targeted drugs and methods of immunotherapy of oncological diseases, the development of cytostatic agents with broad range of actions is an important challenge for the treatment of cancer. Naturally occurring products and their synthetic analogous are excellent sources for new drug candidates, especially for anticancer therapy. The spirooxindole, azabicyclohexane, spirocyclopropapyrrolizine or indenoquinoxaline units are heterocyclic systems that form the core of large families of naturally occurring products with strong bioactivity and interesting structural properties. Significant recent advances in the synthesis of such fused heterocyclic systems led to increased interest in the development of related compounds as potential medicinal agents or biological probes. We have developed a simple and efficient synthesis of complex spirocyclic compounds via stereoselective one-pot three-component 1, 3-dipolar cyclo addition of in situ generated azomethine ylides onto cyclopropenes. The desired spiro [3-aza bicyclo[3.1.0]hexanes] and spiro [cyclopropa[a]pyrrolizines] were produced in good to high yields (up to 96%) and excellent diastereoselectivity (as a single diastereomer) in most cases. The azomethine ylides were in situ generated from 11H-indeno [1, 2-b]quinoxalin-11-one derivatives or isatins and amines, such as N-substituted and N-unsubstituted α-amino acids, various benzylamines, and also peptides (dipeptide Gly-Gly and tripeptide Gly-Gly-Gly). Antitumor activity against erythroleukemia (K562), cervical carcinoma (HeLa) as well as standard fibroblast cell line 3T3B and SV40-transformed 3T3B SV40 cell lines was evaluated in vitro by MTS-assay or flow cytometry. Cell cycle, cell viability and actin cytoskeleton structure were also investigated.
Noha Samy Mostafa
Cairo University, Egypt
Title: Development and validation of a stability–indicating reversed phase HPLC method for simultaneous determination of Ramipril, Atorvastatin and Aspirin in their pharmaceutical formulation
Time : 12:30-13:00
Biography:
Noha Samy Mostafa has completed her MSc in Analytical Chemistry in Faculty of Pharmacy at Cairo University. She is a Teaching Assistant in the Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of pharmacy, Cairo University. She has published two papers in reputed journals.
Abstract:
A specific, sensitive, and rapid stability-indicating chromatographic method has been developed, optimized and validated for simultaneous determination of ramipril (RAM), atorvastatin (ATV) and aspirin (ASP) in their mixture and in the presence of their degradation products. Successful separation of the cited drugs from their degradation product was achieved on X-bridge C-18 analytical column (250×4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm particle size) in an isocratic mode, using mobile phase containing a mixture of acetonitrile-phosphate buffer (pH 2.5, 0.05 M)-tetrahydrofuran (60:40:0.1%, by volume) with UV detection at 218 nm. The linearity of the proposed method was established over the ranges 5–50 μg/mL for RAM and 2-16 μg/mL for both ATV and ASP. The suggested method was validated in compliance with the ICH guidelines and was successfully applied for the quantification of RAM, ATV and ASP in their commercial tablets. The obtained results were statistically compared to those of the official and reported methods; using Student’s t test and F test showing no significant difference with high accuracy and good precision.
Tesnim Dallegi
National Center for Nuclear Sciences and Technologies, Tunisia
Title: 99mTc-labeled tamoxifen derivatives for breast tumor imaging
Time : 14:00-14:30
Biography:
Tesnim Dallegi is an Assistant Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology at National Center for Nuclear Sciences and Technologies in Tunisia. She has completed her Diploma in Biochemistry at the University Tunis El Manar, Tunisia in 2001 and PhD in Molecular Chemistry at the University Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France in 2009. She joined the Department of Radiopharmaceutical in Nuclear Center of Tunisia as Senior Assistant in 2013. She is the Deputy Director of Unit Pilot of Production of the Radiopharmaceutical Kits in Technology Park, Sidi Thabet.
Abstract:
Breast cancer is the fifth most common cause of death from cancer overall. Breast tumors are traditionally classified according to their estrogen receptor status: hormone-dependent tumors (ER+), and hormone-independent tumors (ER-). These receptors serve as targets for endocrine therapies of these cancers. But they also can be used as targets for diagnostic imaging and radiotherapy. For example, antiestrogens such as tamoxifen are largely used for the treatment of women suffering of ER breast cancer. It is known that prolonged treatment with tamoxifen develops drug resistance. In order to overcome drug resistance phenomena and to find new types of drugs, we have developed organometallic analogs of tamoxifen based on ferrocene derivatives. The first examples were hydroxyferrocifen and ferrocenyl diphenol which exhibit an antiproliferative effect against both hormone dependent and hormone independent breast cancer cell lines. Pursuing our research on ferrocene derivatives, the point of interest in this type of compounds is their suitability for a transformation into its technetium analog, via a known metal exchange reaction. In molecular radioimaging, 99mTc is the most widely used radionuclide, owing to its cheapness, easy availability and suitable physical characteristics (t1/2=6.0 h, Eγ=140.5 keV). The search for improved or more tunable radiopharmaceuticals is still currently undertaken and recent research has been directed to radiopharmaceuticals based on compounds containing the CpTc(CO)3 group or Tc(CO)3 core because of the high stability of these moieties. Taking into account this important application, we thought it would be interesting to prepare several compounds and examine their potential as radiopharmaceuticals. Diagnostic imaging can be achieved by an administration of a suitably radiolabeled ligand that accumulates in the receptor-positive tumor where it can be detected and quantified by imaging. Such images can sometimes be used to predict whether hormone therapy is effective. Therefore, the development of such hormone receptor ligands for diagnostic imaging is a promising area of research.
Amal Mahmoud Abou Al Alamein
Cairo University, Egypt
Title: Validated eco-friendly chromatographic methods for simultaneous determination of sacubitril and valsartan in spiked human plasma and in pharmaceutical formulation
Time : 14:30-15:00
Biography:
Amal Mahmoud Abou Al Alamein has completed her PhD and Postdoctoral studies from Cairo University, Faculty of Pharmacy. She has academic experiences in teaching analytical chemistry courses for undergraduates and post graduates. Her research interest is based on method development and validation of different analytical techniques as: Chromatography; UV-Spectrophotometry; Chemometrics and Potentiometric methods with ion selective electrodes (ISEs) and screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) incorporated with carbon nanotubes as potentiometric sensors. She has published more than 20 papers in reputed journals and has been serving as a reviewer and editorial board member in international scientific journals.
Abstract:
Two eco-friendly chromatographic approaches are developed for simultaneous quantification of sacubitril (SAC) and valsartan (VAL) in combined formulation. The first method depended on isocratic HPLC separation of the two medications on the reversed phase InertsiL ODS-3 column C18 (5 μm, 150 mm × 4.0 mm, i.d.) at ambient temperature utilizing a green mobile phase consisting of methanol:ethanol:water (40:30:30, by volumes) +0.1% triethyl amine, pH 3.5 with UV detection at 267 nm. Linearity was attained for both drugs at concentration ranges 1–300 μg.mL−1 in tablets formulation and 0.25–50 μg.mL−1 in spiked human plasma. Second method was HPTLC which based on separation of the two analytes with densitometric measurements of their resolved spots at 260 nm. Complete separation was performed on HPTLC plates (10 cm × 10 cm), 0.1 mm nano silica gel with particle size 6–9 μm F254 (Merck) using ethyl acetate:methanol:glacial acid (9:1:0.1, by volumes) as a green mobile phase. The data of linear regression analysis was used for the regression line in concentration range of 1.5–4.5 and 0.8–4.5 μg.spot−1 for sacubitril and valsartan, respectively and 9–75 ng.spot−1 for both drugs in spiked human plasma.
Heba Abdel-Hady
Theodor Bilharz Research Institute, Egypt
Title: GC-MS analysis, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Mentha spicata
Time : 15:00-15:30
Biography:
Heba Abdel-Hady is a Researcher of Medicinal Chemistry at Theodor Bilharz Research Institute (TBRI). She has completed her graduation with a BSc in the Faculty of Science at Al-Azhar University (Girls Branch), Postgraduation in Biological Application of Natural Products with an MSc. She has carried out research work on isolation and purification of the different classes of natural products which isolated from the medicinal plants. In details, her research interests with bioactive effect of the natural products as well as treatment and preventive of diagnostic diseases and also, evaluation of the toxic effect of any extract or isolated compound in-vivo on all physiological parameters. She has participated as a member in three research project funded by TBRI. She has supervised two PhD theses. She has served as an Editorial Board Member and Reviewer in some journals.
Abstract:
Mentha spicata medicinal properties are well known. In this study, total phenolic and flavonoid contents and the antioxidant activity of the methanol extract of Mentha spicata were determined as well as evaluation of the cytotoxic activity of it. Also, the identification of some bioactive compounds in the plant was analyzed. The antioxidant activity was determined by two methods, DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) and ABTS (2-2'Δazinobis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6- sulphonic acid) while, the cytotoxic assay was determined by MTT assay on HepG-2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma) and MTC-116 (human colon carcinoma). Regarding to the chemical identification of methanol extract was carried out by GC-MS analysis. The results proved that Mentha spicata has high total phenolic and flavonoid contents (388.20±2.38 mg GAE/g of extract & 204.01±17.93 mg RE/g of extract) respectively. Also, exhibited promising antioxidant activity by DPPH & ABTS (IC50=51.13±1.29 μg/ml & 184.31±0.81 μg/ml) respectively. The methanol extract of the plant showed a good cytotoxic effect on HepG2 and HTC-116 (IC50=25.2±3.6 μg/ml & 62.1±4.9 μg/ml) respectively. GC-MS analysis of the methanol extract of Mentha spicata showed 43 oxygenated hydrocarbon compounds. The major ones are hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester (palmitic acid ester) (31.51%) followed by 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid, methyl ester (CAS) (methyl linolenate) (22.10%), 2-Pentadecanone, 6,10,14-trimethyl-(CAS) (6.82%), phytol (6.20%), 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)-, methyl ester (6.18%), hexadecanoic acid (palmitic acid) (5.95%) and methyl stearate (4.49%). The result demonstrated that Mentha spicata is a potential antioxidant and anticancer agents.
Mokhtar M Mabrouk
Tanta University, Egypt
Title: Simultaneous determination of pantoprazole and ketorolac by Reversed phase liquid chromatography in bulk, laboratory prepared mixture and spiked human plasma
Time : 15:30-16:00
Biography:
Abstract:
A highly sensitive, simple and accurate reversed phase liquid chromatographic method has been developed for determination of pantoprazole and ketorolac in their laboratory prepared mixture and spiked human plasma. This method involves separation of pantoprazole and ketorolac on Thermo ODS Hypersil C18 reversed phase column (4.6×250 mm, particle size 5 μm) using a mobile phase consisting of methanol:phosphate buffer (50 mM; pH 5.5) in a ratio of 60:40 (v/v). The flow rate was 1 mL/min with UV detection at 250 nm. The calibration curves were linear from 0.5 to 100 μg/ml for pantoprazole and from 0.5 to 50 μg/ml for ketorolac. The mean % recoveries for mixtures of both drugs at a ratio 2:1 were found to be 99.29±0.43 and 99.32±0.21 for pantoprazole and ketorolac, respectively using the proposed HPLC method. By applying the method to spiked human plasma using the same optimized chromatographic conditions, the calibration curves were linear from 2 to 70 μg/mL for pantoprazole and from 1 to 60 μg/ml for ketorolac. The mean % recoveries for mixtures of both drugs were found to be 100.08±1.92 and 100.25±2.37 for pantoprazole and ketorolac respectively. The developed methods were successfully applied for the determination of pantoprazole and ketorolac in laboratory prepared mixtures containing all possible excipients present in the tablet dosage form.
Mayuri Gupta Pathak
Patan Academy of Health Sciences, Nepal
Title: A comparative study on efficacy of polymyxin B, neomycin and polymyxin B, neomycin, hydrocortisone in the treatment of otitis externa
Time : 16:00-16:30
Biography:
Mayuri Gupta Pathak obtained MD in Clinical Pharmacology from Nepal Medical College Teaching Hospital (NMCTH), Kathmandu, Nepal in 2015. I obtained MBBS from Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital (KMCTH), Kathmandu, NEPAL in 2006. Currently working as Lecturer at Patan Academy of Health Sciences (PAHS), Kathmandu Nepal. Worked as a tutor in Clinical Pharmacology before starting MD for 3 months in NMCTH. Her trainings include Neonatal advanced life support in KMCTH, Interdepartmental clinical meeting on “Diabetics and Anesthesia” in KMCTH and advanced cardiac life support in Anesthesia in NMCTH. She have also done oral presentation at Las Vegas, USA in 2016.
Abstract:
Introduction: Acute otitis externa is a common condition involving inflammation of the ear canal. The acute form is caused primarily by bacterial infection, with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus the most common pathogens. Acute otitis externa presents with the rapid onset of ear canal inflammation, resulting in otalgia, itching, canal edema, canal erythema, and otorrhea, and often occurs following swimming or minor trauma from inappropriate cleaning. Tenderness with movement of the tragus or pinna is a classic finding. Neomycin/polymyxin B/hydrocortisone preparations are a reasonable first-line therapy when the tympanic membrane is intact. Oral antibiotics are reserved for cases in which the infection has spread beyond the ear canal or in patients at risk of a rapidly progressing infection.
Aim: To compare the efficacy of polymyxin B, Neomycin and Polymyxin B, Neomycin, Hydrocortisone in the treatment of Otitis externa.
Methodology: This study was carried out in the Department of ENT, Nepal Medical College Teaching Hospital (NMCTH), Attarkhel, Kathmandu, Nepal from August 2012 to May 2014. This, prospective randomized study included patients with otitis externa. Patients of all age groups and both gender were included in this study. Patients were randomized into two groups; Group A: Patients, who received Polymyxin B, Neomycin and Group B patients, who received Polymyxin B, Neomycin, Hydrocortisone. Pack soaked either with polymyxin B neomycin/ hydrocortisone and applied for 48 hours. If not recover again applied for next 48 hours. The study will be conducted on the patient diagnosis, clinical features- signs: 1. Tragal tenderness. 2. Circumduction tenderness. Thus, the efficacy was compared between two drug groups.
